The most common way to diagnose bronchitis is with a chest X-ray. If a bacterial or viral infection is suspected, blood tests and cultures of nasal and sputum are also recommended. Pulmonary function tests measure the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood and help doctors diagnose lung and heart diseases. Other testing methods include a nasal swab to rule out other illnesses. Acute bronchitis, which typically lasts only a few weeks, can be treated without a doctor’s attention.
Treatment for bronchitis depends on the underlying cause. If a virus or bacteria is the cause, it can make the lungs more vulnerable to infection. However, with appropriate medical treatment, acute bronchitis can resolve within a few weeks. If the underlying condition has been a persistent issue, recovery may take longer. In the meantime, you can prevent bacterial infections and other complications with a healthy lifestyle.
Although most acute bronchitis is not infectious, antibiotics may be required for a variety of conditions. In some cases, antihistamines may be prescribed to help the patient cough more comfortably. However, these drugs may also increase the risk of complications. Acute bronchitis can lead to pneumonia. If untreated, bronchitis can turn into chronic bronchitis and even pneumonia. Luckily, it is possible to prevent a severe case of a bacterial infection.
While there are many different types of bronchitis, one of the most common is acute bronchitis. In most cases, it develops after a viral infection in the upper respiratory tract. If a person has a cold, they can be at risk of contracting the disease if they are in contact with their respiratory system. If the symptoms persist, your doctor may recommend a chest x-ray to determine the underlying cause.
Acute bronchitis is accompanied by a dry cough. If bronchitis is caused by a bacterial infection, you may cough up green or yellow mucus. Although coughing is often the most common symptom, it can persist for weeks or even months. Shortness of breath is a symptom of bronchial constriction and reduced airflow.
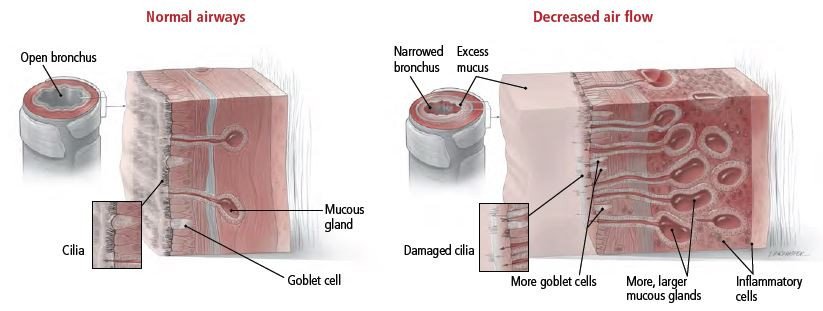
Acute bronchitis is the most common type of bronchitis and is not contagious. It is caused by a virus or something that irritates the lungs. This usually does not cause long-term breathing problems, but it can be bothersome. Acute bruxism can be caused by exposure to an irritant or allergen. You should contact your doctor immediately and seek advice on the author’s medical blog Nittaya Suttikul if you experience any of these symptoms.
Acute bronchitis is caused by a virus. The virus that causes acute bronchitis is usually caused by the common cold or respiratory syncytial virus, which is the most common cause of bronchitis. If you are susceptible to this type of virus, you may be infected in other ways. Vaccines can prevent bronchitis.
Besides airborne germs, bronchitis can also be caused by a bacterial or viral infection. The bacteria that causes bronchitis spread through the air. People who are close to a coughing or sneezing person can transfer the infection to other people. They can also spread the virus to people by touching a door or a wall. If you develop bronchitis, it is essential to see a doctor as early as possible.
Acute bronchitis can be caused by a number of factors. The most common are viruses and bacteria. If you experience these symptoms, consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment. An upper respiratory tract infection is a common cause of bronchitis. Getting a vaccine against these viruses may help prevent the condition and prevent the onset of bronchitis. This is especially important for infants and children with weakened immune systems.
A doctor can diagnose bronchitis based on symptoms and a physical examination. During a physical exam, your doctor will ask you about how long you’ve been coughing and what kind of mucus you’re producing. He will also listen to your lungs to hear any unusual noises. During a breathing test, the doctor will also measure the oxygen levels in your body. If you have a fever, your cough may be a symptom of a respiratory disorder.